Many organizations use firewalls to protect themselves from harmful traffic flow on the internet. However, many firms adopted on-premise firewalls before the rapid proliferation of:
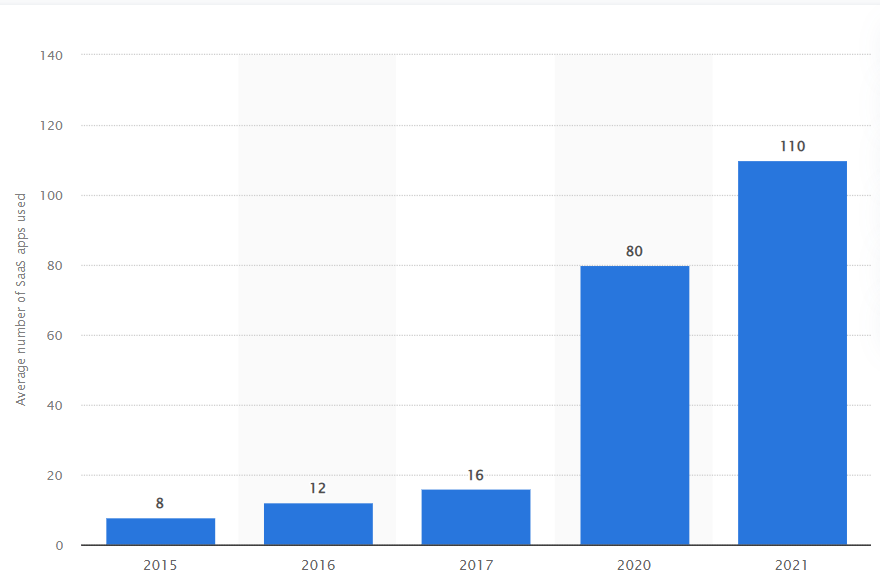
- Public cloud solutions (AWS, Azure, Salesforce) for daily business operations (see Figure 1).
- Remote/hybrid working.
These new trends made on-premise firewall solutions ineffective. Therefore, in this article, we introduce firewalls as a service (FWaaS) in depth and compare them with on-premise (hardware) and host-based firewalls to provide a better understanding.
Figure 1: Average number of Saas platforms used per entities.
What is a firewall?
A firewall is a system that filters information from the internet. It prevents unauthorized access from entering a private network. Thus, a firewall’s purpose is to create a safety barrier. It is possible to design filters by considering the following (see Figure 2):
- IP addresses
- Domain names
- Protocols
- Programs/services
- Ports
Figure 2: Filtering options for the firewall programs

To learn how firewalls protect users’ private network, check out our guide that explains how a firewall work step by step.
What are the differences between FWaaS, on premise and software firewalls?
The main difference between these types of firewalls is their protection areas.
- Host-based firewalls: These types of firewalls are installed on a single computer. They can be an effective cybersecurity solution for firms with few employees. Additionally, some companies (with very sensitive data) or high-ranking executives may require host-based firewalls in addition to on-premise or cloud-based firewalls to secure private information from outsiders.
- On-premise firewall: It is a network layer tool that uses a combination of software and hardware (servers) technologies. As a result, an on-premise firewall safeguards all devices in a greater area (an office for instance). It is suitable for traditional working where employees work in an office building. Similarly, military organizations or intelligence services of states can use such tools. However, geographical distance brings latency problems due to backhauling user traffic.
- FWaaS: A cloud-based firewall is another name for it. FWaaS works independently of the network it protects. As a result, FWaaS systems filter internet traffic for their users from any location with the least amount of traffic latency. They are more easily integrated with cloud platforms due to their cloud native characteristics. In general, FWaaS products are appropriate for firms that embrace remote/hybrid working or have a large number of branches or offices in different geographical areas.
8 main benefits of FWaaS
- Lower cost: On-premise firewall systems require expensive hardware components and a skilled IT team to deploy and manage the system. Firms who use FWaaS, on the other hand, just use the provider’s IT team and physical components. Consequently, the organization’s only expenditure becomes the monthly subscription price.
- Easy deployment: FWaaS users do not need to deploy hardware, so a few mouse clicks should be enough to use it.
- Scalability: When a company’s internet bandwidth grows, it must purchase high-performance hardware in order to continue using its on-premise firewall. Companies, on the other hand, can effortlessly arrange their bandwidth capacity by using FWaaS. Additionally, when companies open new branches, entering the new configuration into the cloud provider’s system is sufficient for FWaaS users.
- Ease of upgrade: As service vendors provide different features for different subscription packages and switching between them is relatively easy.
- Improve user experience: Backhauling user traffic is not required with FWaaS. This lowers latency concerns and possible data losses.
- Ease of integration with cloud platforms: FWaaS providers design their products in a way that can easily integrate with major cloud platform tools.
-
Ease of integration with other cybersecurity solutions: FWaaS systems are designed for integrating with other cloud based cybersecurity tools such as:
- Secure access service edge (SASE)
- Zero trust network access (ZTNA)
- Secure web gateway (SWG)
- Software defined perimeter (SDP)
to provide a complete zero trust cybersecurity architecture.
- Better ESG posture: Environmental and social factors have a substantial impact on a company’s market share and profitability. According to a recent Accenture report, public cloud devices are more environmentally friendly than on-premise tools. Analysis suggests that the migration of all facilities from on-premise to the cloud reduces CO2 emissions by the equivalent of removing 20 million automobiles from the road.
6 Things you must consider before choosing a FWaaS vendor
- Integrability: Businesses use a range of public cloud tools for their operation. As a result, it’s crucial to ensure whether the candidate FWaas vendor’s solution works well with the other cloud technologies you employ.
- Certificates: ISO 27001, 27002, and HIPAA certifications verify your candidate partners’ ability to manage sensitive information. To prevent data leakages, it is crucial to investigate such certifications before initiating a relationship.
- References: Companies can use previous clients and case studies to guide them in choosing an FWaaS supplier. Communicate with vendors’ customers, see if they have any customers in the same industry as you, and so on.
- Product features: FWaaS systems might have different filtering capabilities. Thus, before working with a vendor, check your compliance requirements and industry/business needs.
- Customer support model: Some companies have a proactive customer service strategy, whereas others do not. The demand for complete customer service can differ depending on your company’s IT capabilities. Therefore, firms should evaluate customer support capabilities before collaborating with a provider.
- Cost: For any investment companies, perform a benefit-cost analysis. Thus, it is essential to compare the prices of the different vendors.
Read from original source here.

